Table of Contents
Project management is all about piecing a puzzle together with many tasks, deadlines, and dependencies that need to be solved. This is where project management tools such as PERT (Program Evaluation Review Technique) and Gantt charts are essential. Moreover, these charts can act as roadmaps, allowing teams to visualize project timelines, organize tasks, and monitor progress.
Furthermore, if you are a student completing a school project, a professional coordinating a team, or an entrepreneur balancing several tasks, being familiar with these tools can take the burden off and simplify your work. Therefore, through this blog by All Assignment Help, we will take you through the step-by-step process of creating PERT and Gantt Charts for the project, making you plan and execute like a pro!
Understanding PERT Charts
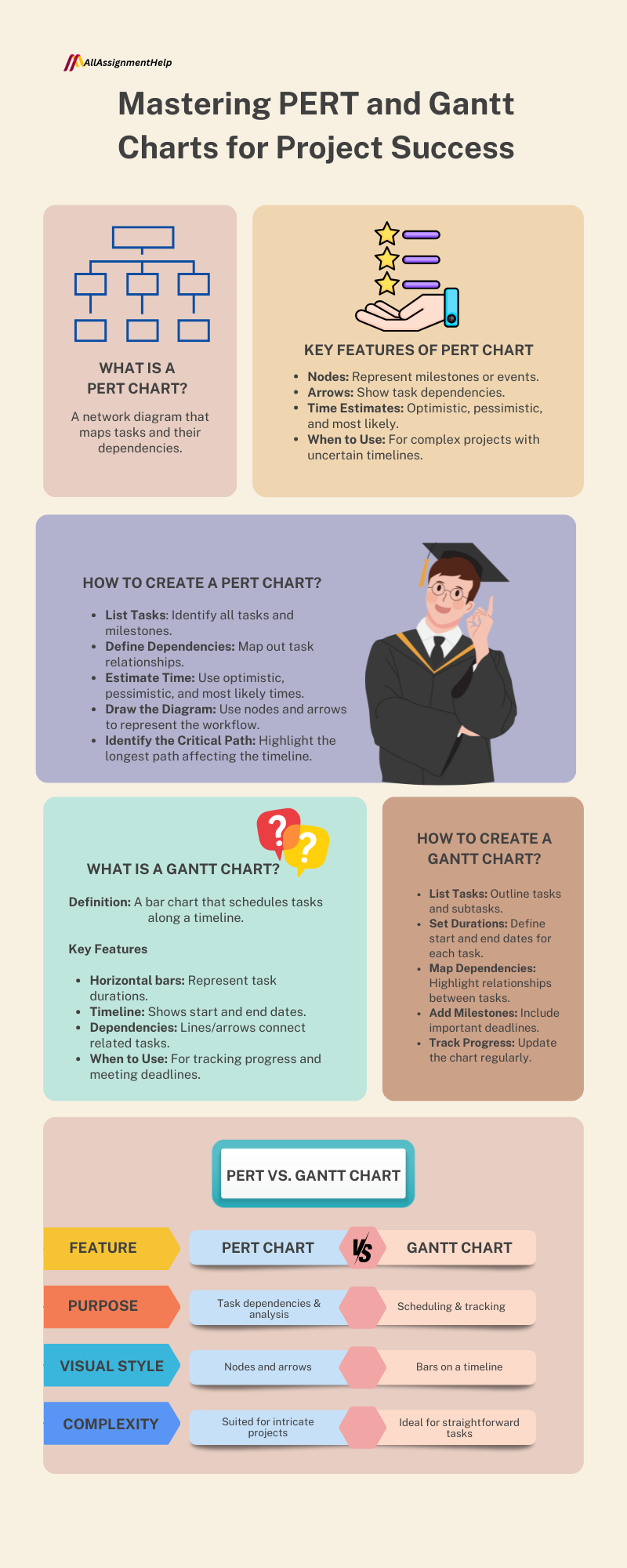
What is a PERT chart?
The PERT (Program Evaluation Review Technique) chart is a visual project management tool that helps in defining the work that needs to be done to complete the project. Moreover, it lists dependencies between tasks and the number of hours needed to complete every task. Furthermore, in need of redefining and managing complex workflows and designs under stricter time deadlines, PERT charts are quite handy as they show the sequence of activities.
Key components of a PERT chart
- Nodes: Denote project events or milestones. These are locations where a task begins or ends.
- Arrow: What activities tie milestones together and show dependencies?
- Time estimates: Provide three categories of estimates. Optimistic Time(O): The minimum time for which a task can be completed. Pessimistic time (P): The maximum possible time a task will take. Most Likely Time (M): It is the time which is most frequently taken by to process the task.
Benefits of using PERT charts
- Visual clarity: Makes it easier to visualize the order of work with dependencies.
- Critical path identification: Assists in determining which tasks are critical for on-time project completion.
- Improved time management: Integrates different estimates to encourage realistic scheduling.
- Mitigate risks: Identifies possible bottlenecks in advance and enables proactive changes
Hence, once we know these fundamentals, the challenge of PERT charts becomes nothing more than a collection of tasks that keeps you organized from beginning to end.
Creating a PERT Chart
Step-by-step guide to creating a PERT chart
Step 1: List all tasks and milestones
- The first step is to list all the tasks necessary to complete your project.
- Define milestones that show progress by splitting the project into smaller, achievable tasks.
Step 2: Determine task dependencies
- Determine what tasks must be completed before each task will begin.
Step 3: Estimate task durations
- Use the method of estimating three times.
- Optimistic time (O) — the best-case scenario or how long the task will take in an ideal world
- Pessimistic time (P): The maximum time it would take.
- Most likely time (M): the best guess.
- Utilize the expected time formula (TE): TE=O+4M+P6TE = \frac{O + 4M + P}{6}
Step 4: Draw the PERT chart
- Use circles to indicate tasks and milestones in your work.
- Indicate the sequence and dependencies with arrows linking nodes.
- Assign the names of the tasks and the duration it might take to complete each of the tasks and represent them as label arrows.
Step 5: Identify the critical path
- Ascertain the time taken to travel from the start to the end for each of the available routes.
- Critical path is the longest path, those tasks are critical and can affect the project schedule.
However, if you find curating PERT and Gantt Charts a matter of complexity, you can hire professionals to get help with coursework and curate a required chart for you to simplify your work.
Tips for effective PERT chart creation
- Keep it updated: Update the chart regularly whenever the actual progress has been made or task durations needs to be change.
- Use software tools: Tools such as Lucidchart, SmartDraw or Microsoft Visio could make the creation of a PERT chart easier.
- Focus on the critical path: Make sure that critical path tasks are given priority so that projects are not held up.
Therefore, with these steps in mind, you can create a well-prepared PERT chart ensuring the maximum possible project planning and execution.
Also read: How to Write a College Resume – A Guide for College Students
Understanding Gantt Charts
What is a Gantt chart?
A Gantt chart is type of a bar chart that can show a project schedule visually. Moreover, showing dates for when tasks will begin and end, durations, and dependencies it lays things out on a timeline. Furthermore, Gantt charts are an essential tool for many project management processes, as they allow teams to see how everything fits into the scope of work and helps ensure that project tasks are delivered on time.
Key features of a Gantt chart
- Task bars: Horizontal bars indicate tasks, with the length representing the duration of each task.
- Timeline: A horizontal line displays the timeline for the project, which is often divided by days, weeks, or months.
- Dependencies: Related tasks are joined with arrows or lines, indicating which tasks are reliant on one another.
- Milestones: A milestone is a marker that indicates that an important event in a project has occurred, or the deadline at which a deliverable will be produced.
- Progress indicators: Visuals indicating how much of a task has been completed, usually in the form of shaded areas within task bars.
Advantages of Gantt charts
- Simplicity in scheduling: This gives a visual representation of the time frame of tasks and where they overlap
- Tracking progress: Allows you to track completed, ongoing and pending tasks.
- Resource management: Helps to allocate resources efficiently by determining the time and place required for their utilization.
- Teamwork: Makes people on your team work together, keeping everyone on the same page when it comes to deadlines and priorities.
Additionally, if the projects become too much to handle for you, try using an online assignment help service for the composition of your PERT and Gantt Charts.
When to use a Gantt chart
- For projects with specific deadlines and deliverables
- You must check progress more frequently.
- To organize team roles and know which tasks depend on which ones.
Additionally, a Gantt chart is an effective visualization tool to understand the project timeline and facilitates task management for the team so that everyone is on the same page to achieve the project goal.
Also read: What is a Hypothesis and How to Write a Hypothesis
Creating a Gantt Chart
Step-by-step guide to creating a Gantt chart
Step 1: Identify tasks and subtasks
- Start with listing everything that needs to be done to complete the project: tasks, subtasks, etc.
- Combine related tasks together.
Step 2: Define task durations
- One must plan a realistic time of completing each task and schedule start and end dates for it after the task and noting the time in order.
- Ensure the timelines are based on reality and this is what makes sure no unnecessary delay happens.
Step 3: Determine task dependencies
- Find out what needs to be done before doing other tasks.
- Identify sequential, overlapping, or independent tasks in an unmistakable manner
Step 4: Draw the chart
- Tasks listed vertically on the list; time frame spans horizontally across the chart.
- Draw horizontal bars representing the total time span of each given task on the timeline.
- Draw arrows or lines between dependent tasks.
Step 5: Add milestones and deadlines
- Mark prominent project milestones, like major deliverables or decision points.
- Set deadlines to ensure that the team remains focused on meeting tasks conducted in a timely fashion.
Step 6: Track progress
- Regularly update chart according to the up-to-date status of the tasks.
- In the case where you want to represent task progress levels, this can be achieved using color coding or shading inside task bars.
Tools for creating Gantt chart
Software options:
- Microsoft Project: Best for complex projects with multiple tasks.
- Smartsheet is an all-in-one tool where teams can work together.
- Trello (Gantt chart plugins): Best for agile projects
Spreadsheets:
- You can manually create basic Gantt charts using Excel or Google Sheets.
In addition to this, if you have other responsibilities, like attending your online classes, which are hindering you from composing your PERT and Gantt Charts and carrying out your project, you can seek expert assistance. In terms of difficulty, you can pay someone to take your online class. The online class takers will timely handle your classes, and you may fully focus on your PERT and Gantt charts better.
Tips for effective Gantt charts
- Keep it simple: Do not put more on the chart than is essential to your task and to understanding the milestones.
- Frequent updates: Keep the chart updated with the latest changes.
- Engage the team: You can also share this chart with the team to get everyone on the same page in terms of expectations and timelines.
Therefore, using these steps along with the correct tools, you can generate a Gantt chart as a plan for your project that indicates the way things will be carried out and eventually completed.
Comparing PERT and Gantt Charts
Though they are similar in how they are both useful for project management tasks, PERT and Gantt Charts are different, and are appropriate for different kinds of projects. Moreover, the difference between them will help you to know when to use which.
Purpose
- PERT charts: Used to plan and analyze the tasks involved in completing a project—usually for complex projects where time needed to complete different tasks is uncertain. Moreover, this focus is on dependencies of tasks and critical paths.
- Gantt charts: Used mainly for scheduling and tracking progress, and providing a visual timeline of tasks, these live dashboards help monitor real-time project status.
Visualization
- PERT charts: Presents tasks as a flow diagram of nodes and arrows to show relationship (dependency) and flow (task sequence).
- Gantt charts: They are great for showing tasks on a timeline (with horizontal time) and making the duration and overlapping of the tasks clearer.
Key strengths
PERT charts:
- Great for determining paths and delays.
- Include time estimates (optimistic, pessimistic, most likely).
- Well adapted to projects in which the let-one timeline is unknown or malleable.
Gantt charts:
- Communicate the precise and comprehensive task schedule.
- Good for monitoring progress and deadlines.
- Helps in optimizing resources and teamwork
Complexity and use case
PERT charts:
- More sophisticated and evaluative, appropriate for projects that require more than one dependency or are more research-intense or complex.
- Typically used in the field of engineering, R&D, construction industry
Gantt charts:
- Easier and more user-friendly, it is best for simple projects with a clear timeline.
- Widely used in industries such as marketing, education, and software development.
Although PERT and Gantt Charts are primarily project management charts, they can be a very effective way to structure learning and problem-solving in anatomy and trigonometry, giving you a way to manage time and dependencies between topics. Also, suppose you are someone facing issues with your anatomy and trigonometry assignments. In that case, you can seek help from anatomy assignment help services and trigonometry homework help platforms to achieve subject excellence.
Tools and software
- PERT chart: Typically use tools such as Lucidchart or Visio to build network diagrams.
- Gantt charts: Simple to draw out in Microsoft Project, Smartsheet, and even Excel.
When to use each
- Identify the critical path, build a PERT Chart when their time frame is unclear or they carry a lot of dependencies to other tasks
- Choose a Gantt chart if you want a timeline with deadlines that you can use to monitor progress.
Therefore, knowing the differences between these allows you to choose the right tool to use in the project, which makes planning, execution, and management simpler.
Conclusion
So, you can turn your project management upside down by mastering PERT and Gantt Charts. Although PERT chart aids in planning and analyzing complex tasks emphasizing task dependency and critical paths, Gantt chart gives a timeline and help to monitor progress and remain on schedule. Moreover, everything in both tools has its own strong point, and understanding about the timing & the way to use them can largely enhance both, your productivity as well as decision-making skills. Also, no matter if you are working on a tough academic task, a business meeting project, or a team project, these charts are here to save you! So, draw your PERT and Gantt Charts now, and see how your projects can be seamless!
Frequently Asked Questions
| Question: Is it possible to use both PERT or Gantt charts in one project? Answer: Yes, you can use both. PERT charts are best for planning and analyzing dependent and non-dependent tasks, while Gantt charts manage progress and timelines. Combined, they give you a complete picture of your project. |
| Question: Suggest the best software for PERT and Gantt Charts Answer: Regarding PERT charts, Lucidchart and Visio work great. Options for Gantt charts include Microsoft Project, Smartsheet, or even Excel, all of which provide built-in tools for organizing, scheduling, and tracking your projects in granular detail. |
