Table of Contents
Mobile communication is one of the most important aspects of modern life and has been highly significant and relevant to every aspect of business and normal life. It is the application of technology that helps in communicating with others in several locations without using any kind of physical connection, such as cables or wires. Mobile communication systems have made life convenient and easier, saving effort and time. In this blog post of All Assignment Help, we will deeply look into this important innovation of modern technology. Here, we will discuss everything about mobile communication technology, from its history to future impacts.
What is Mobile Communication?
Mobile communication is a technology that enables us to speak with people who are in different locations without requiring a physical connection, such as wires or cables. It offers wireless communication. Ultimately, this saves time and effort and makes our lives easier.
A mobile phone is an example of mobile communication (wireless communication). It is also referred to as a mobile cellular network, cell phone, or handphone. It is an electric device that facilitates full duplex two-way radio communication using a cellular network of base stations called a cell site.
If you want to pursue a career in Information technology, mobile communication would be there as a prime subject of learning. However, a mobile communication assignment often involves writing tasks on topics such as signal processing, network protocols, and wireless technologies. These assignments can be complex. Students must hold technical expertise and required research skills to write informative assignments on these topics. Don’t worry! They can always opt for programming assignment help services online where they will be assisted by subject experts who will solve their assignment writing problems easily and timely.
Read Here: Mobile Learning – How Learning Happens Through a Smartphone?
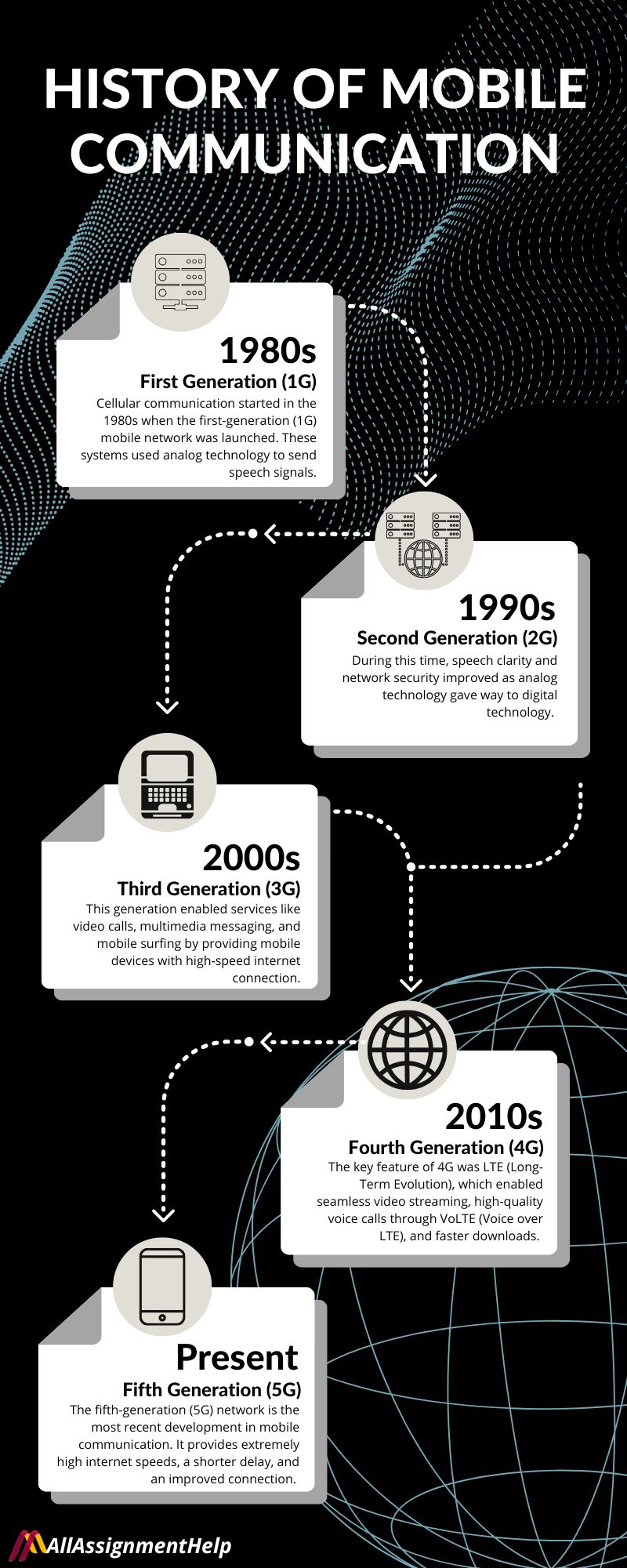
History of Mobile Communication
Mobile communication has changed across multiple generations, with each one transforming how individuals communicate. Let’s have a brief look at the history of mobile communication and how it has evolved over the time:
Early Developments (Pre-1940s)
The invention of wireless telegraphy in the early 20th century marked the beginning of wireless communication. The primary uses of this technology were in military applications and ship-to-shore communication. The usage of radio waves for communication increased, particularly in emergency services and law enforcement.
First Generation (1G) – 1980s
Cellular communication started in the 1980s when the first-generation (1G) mobile network was launched. These mobile communication systems used analog technology to send speech signals. Thus, it had some drawbacks, such as poor sound quality, frequent call dropouts, and safety concerns. Despite its drawbacks, 1G set the stage for later developments in wireless communication technology.
Second Generation (2G) – 1990s
The advent of second-generation (2G) networks in the 1990s significantly changed mobile communication. During this time, speech clarity and network security improved as analog technology gave way to digital technology. The Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) made it possible for mobile users to connect across national borders.
Third Generation (3G) – Early 2000s
The launch of 3G networks in the early 2000s marked a significant advancement in mobile communication. This generation enabled services like video calls, multimedia messaging, and mobile surfing by providing mobile devices with high-speed internet connection. Moreover, the 3G era prepared the ground for the smartphone revolution. It increases the accessibility of internet services on mobile devices.
Fourth Generation (4G) – 2010s
The 2010s saw the development of fourth-generation (4G) networks. It increased the network’s dependability and allowed for higher data rates. The key feature of 4G was LTE (Long-Term Evolution), which enabled seamless video streaming, high-quality voice calls through VoLTE (Voice over LTE), and faster downloads. Also, this period saw the rise of social media platforms, cloud computing, and mobile applications.
Fifth Generation (5G) – Present
The fifth-generation (5G) network is the most recent development in mobile communication. It provides extremely high internet speeds, a shorter delay, and an improved connection. 5G technology facilitates new developments such as remote healthcare, smart cities, driverless cars, and the Internet of Things (IoT). Furthermore, it helps consumers and organizations take advantage of the digital revolution by offering a more effective and responsive mobile experience.
The Future of Mobile Communication
(6G and Beyond)
The future of mobile communication is set to be shaped by sixth-generation (6G) networks. It will offer promising faster speeds and seamless integration of artificial intelligence (AI) for enhanced, and intelligent connectivity.
Future uses for 6G can include continuous worldwide connection, space-based networks, and holographic communication. As mobile technology develops further, it will transform more sectors and enhance daily life.
Also, the future of mobile communication with 6G technology is set to transform online learning, making it faster, smarter, and more interactive. Imagine attending online classes with zero lag, experiencing 3D holographic lectures, and getting instant AI-powered tutoring. This is what 6G can bring to education.
Not only this, students who face challenges in their online classes can get access to a wide range of online class help services within just a click. With just one Google search, where should I hire someone to take my online class for me? they can connect with reliable class help services where they can hire an online class taker of their own choice to complete the coursework, help with assignments, take exams, or participate in online discussions. These services will ensure that students get the academic assistance they need anytime, anywhere.
Classifications of Mobile Communication
Mobile communication is classified into two types:
Infrastructure mobile communication
It requires infrastructure to establish its network and let people communicate with each other. Cellular mobile communication is one of the best examples of infrastructure wireless mobile communication. Cellular communication uses a base trans-receiver system (BTS), which has two categories: vertical antennas and drum antennas, for its communication process.
Infrastructure-less mobile communication
This type of communication eliminates the need for infrastructure for its communication process. It is cost-effective and is classified into two types: mobile ad hoc networks (MANET) and wireless sensor networks (WSN).
The MANET is used for emergency purposes and is categorized into Flying Adhoc Networks (FANET), Smartphone Adhoc Networks (SANET), and Vehicular Adhoc Networks (VANET).
Wireless sensor networks (WSN) are small and cost-effective. They are known to provide hassle-free communication experiences. WSN analyses, collects, and transmits data and is used in remote environments.
Both of these fall under the study of computer networking. Hence, you need to have a strong understanding of computer networking, its concepts, and principles, especially for assignment writing. However, if you lack an understanding of the related concepts and principles and fail to write a well-constructed assignment, don’t hesitate to reach out to computer network assignment help services online. These services not only assist in completing your assignments but also help clarify your doubts regarding networking and mobile communication.
Benefits of Mobile Communication
The following are some benefits of mobile communication:
- Flexibility: People can connect with each other no matter where they are via wireless communication. Now, one does not have to be at an office or a phone booth to send and receive messages.
- Cost-effectiveness: No physical infrastructure (wires or cables) or maintenance procedures are required for wireless communication. As a result, the price is lower.
- Speed: There have also been speed improvements. There was a significant improvement in the accuracy and speed of network connectivity. Also, this faster speed of mobile communication system allows students to get help with their assignments instantly. Whether someone needs computer science assignment help or help with programming assignments, the speed and accuracy of mobile communications allow them to get instant help just from their digital devices.
- Accessibility: It is simple to reach faraway locations with the use of wireless technologies. For example, it is now possible to receive education online in remote locations. Teachers and students don’t have to travel to far places to provide their lectures anymore.
- Continuous connection: People can react to situations faster when they are continuously connected. For instance, a mobile phone or other wireless device can guarantee continuous connectivity when you travel or move from location to location, something that a conventional landline cannot do.
Emerging Trends in Mobile Communication
Mobile communication is evolving rapidly, driven by advancements in technology and changing consumer demands. Here are some of the emerging trends in mobile communication:
AI-Powered Communication
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing mobile communication through automation and better user experience. AI-powered chatbots, virtual assistants such as Google Assistant and Siri, and predictive text tools increase productivity and user engagement. Additionally, AI plays a key part in speech recognition, tailored content suggestions, and spam identification. It improves the security and usability of mobile interactions.
Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
The Internet of Things (IoT) allows real-time data exchange and communication across multiple smart devices by connecting them via mobile networks. This technology is widely used in smart homes, wearable devices, healthcare monitoring systems, and industrial automation. For instance, IoT-enabled smartwatches can track health indicators and notify physicians, while mobile applications can be used to remotely operate smart appliances.
Satellite-Based Mobile Networks
The goal of satellite-based mobile networks is to offer seamless access in underserved and rural locations that are difficult for standard cellular networks to reach. Businesses like AST SpaceMobile, OneWeb, and Starlink are developing satellite-powered mobile services that guarantee internet availability anywhere. These networks will be especially helpful for aviation and maritime communication, rural connection, and disaster recovery.
Edge Computing for Mobile Devices
Edge computing boosts real-time processing, lowers latency, and boosts application performance in mobile communication. This is especially important for time-sensitive applications like industrial automation, smart surveillance, and driverless cars. Furthermore, edge computing reduces the need for remote data centers, increasing the dependability and effectiveness of mobile services.
These trends demonstrate how mobile communication has evolved dynamically, influencing how we connect and communicate online. You can also enroll yourself in online courses to learn more about mobile communication technology and its related aspects. There are multiple online courses offered by online learning platforms and universities. Furthermore, you can also hire an online class helper to assist you with your coursework. From taking your online classes to performing your exams online, these online class helpers can do all for you under your budget.
Also Read: GSM: Global System for Mobile: An Era of Cellular Network Technology
Conclusion
Mobile communication offers accessibility, speed, and convenience. It has completely changed how people communicate. From the first wireless telegraphy to today’s advanced 5G networks, each generation has improved communication effectiveness and added new features. Mobile communication will keep changing the digital environment as technology develops, improving connection and efficiency. Its impact is unmatched and guarantees an endless future.
Students pursuing a major in mobile communication for career growth often find the subject complex and challenging. The difficulty increases for those taking the course online, as they have limited opportunities for real-time clarification. Additionally, some students may hesitate to ask questions due to a lack of confidence, further hindering their understanding. If you relate to this and need help with online exams, hire experts for assistance. Simply visit our site and say, take my online exam for me. Our support team will guide you in hiring a professional, ensuring you get the help you need to succeed.
FAQs
Question 1: When did the historical background of wireless mobile communication start?
Answer 1: It started with the introduction of the first telegraph between the years 1600 and 1833.
Question 2: What are the different advantages of mobile communications?
Answer 2: Speed, accessibility, higher productivity, constant connectivity, flexibility, better collaboration, and cost-effectiveness are some of the major advantages of mobile communication.
Question 3: What are some of the major examples of wireless communication in the modern world?
Answer 3: Television, radio broadcasting, satellite communication, radar, cellular communication, and the Global Positioning System (GPS) are some examples of wireless communication.
