Table of Contents
Evolution is a change in the genetic composition of a population and is an important characteristic of human beings. There are different stages in the evolution of humans. Dryopithecus, Australopithecus, Homo Habilis, Homo Erectus, Homo neanderthalensis, and Homo sapiens are the stages that briefly explain the evolution of humans through all these years. Natural selection is the most famous and important mechanism of evolution, which discusses how a combination of alleles of different genes makes an organism survive and reproduce in an environment. Natural mechanisms are not the only ones that help in biological evolution. There is also another evolutionary mechanism known as genetic drift, which studies how allele frequency tends to develop in a finite population over some time.
If you are interested in learning more about human evolution and how allele frequency changes in different generations and helps in survival, then this blog is the right one to read. In this blog post from AllAssignmentHelp.com, we will briefly examine this topic. Here we have discussed introductions, features, causes, and much more related to genetic drift.
Introduction to Genetic Drift
The term genetic drift is also known as the Sewall-Wright effect or Allelic effect. It is the process by which deviations in the expected allele frequencies tend to develop in a finite population over some time. In simple words, it can also be said that genetic drift is the type of variation that occurs in the existing gene variant in the population because of the presence of random sampling organisms. This can be further explained with the different types of examples. For instance, a mother who has blue eyes and a father who has brown eyes can have a child with either blue or brown eyes. In this situation, if brown eyes are the dominant allele, even if there is a 50% chance that a child could have blue eyes, there are also chances that a child could have brown eyes. It is also called sampling error.
Herein, it can also be said that the population’s allele frequency is the fraction of the copies of the one gene that allocates a particular form. Here, we will explore the causes behind the genetic drift. Further, we will also carry on discussion on the two major effects that are related to genetic drift effectively. Details will also be given about the differences that exist between this drift and mutation. Genes and genetic disorders are all interesting fields of study that one can learn more about. However, students studying biology often find themselves in a situation where they get stuck with a topic and neither understand nor neglect it. Have you also been in any of these situations? If yes, you should seek biology assignment help. Seeking assistance will help you earn top grades and also get a thorough understanding of difficult biological concepts.
Features of Genetic Drift
Genetic drift is the study of allelic frequency changes in a group of populations. Multiple kinds of research and studies are conducted in this field that help one understand and apply these concepts practically. Let us now explore some of the features of genetic drift.
- The loss concerning the genetic variation results within the population itself.
- Population size matters in the sampling error. It has been found that the allele frequency changes rapidly in the small population as compared to the large population. The large population is likely not to respond to the changes in allele frequency and survive for reproduction.
- The effects of this drift are stronger in some cases. Genetic drift is common after population bottlenecks.
- The frequency of different alleles is the main cause of sampling error.
- The allele frequency in the genetic drift changes until H reaches zero.
- This also describes random fluctuations in the number of gene variants in a population. It also changes with increases and decreases of genes called alleles by chance over time.
Before moving forward and discussing other things in this blog post, if you are a student and are stressed about who could take my online biology class for me, you can seek online help and improve your grades. Convenience, flexibility, and personalized learning are the three important benefits of hiring someone to do your online biology classes.
Significance of Genetic Drift in Evolution
In the process of evolution, genetic variation is considered one of the most important elements. It enables natural selection with the increase and decrease in frequency of alleles that are already present in the population. Furthermore, it provides individuals with the opportunity to adapt themselves to their surroundings. However, along with the given task, it also assures the survival of the population. Genetic drift is regarded as one of the biggest matters of concern for the survival of the population. The Sewall effect has a direct connection to human evolution. Are you curious about its importance in evolution? Yes, continue reading to learn about this in detail.
- Genes are transmitted from generation to generation, which provides similarity among people. However, genetic drift is a factor that can cause a new population to be completely different from the previous ones.
- Allelic shifts help in the evolution of new species, which can be completely different from the parent population.
- It may also cause gene variants to disappear completely, which will reduce genetic variation.
Also Read: Biology Assignment: A Full Package Guide
Types of Genetic Drift
We have discussed different important things about genetic drift. In addition to those, two major effects characterize the natural phenomenon of population elimination. There is a bottleneck effect and a founder effect. These two are also known as the two types of genetic drift. Each of them has a role in the evolution of the human population. Below, we have provided a detailed overview of these effects.
1- Bottleneck Effect
A genetic bottleneck is the type of evolutionary event in which the size of the population drastically reduces from large to small. The main reason behind this is the presence of environmental factors such as floods, earthquakes, fires, droughts, etc. The given types of factors will tend to cause a reduction in the genetic diversity of the population in comparison to the parent population. On the other hand, the given circumstances will also lead to some alleles being overexpressed in the survival population. However, some alleles are under expressed in the survival population. Additionally, as per the direct aftermath of genetic drift, homogeneity and inbreeding will be increased in these populations. Thus, the given thing will lead to the occurrence of the deleterious mutation effectively. For instance, the diversification of the hyperthermophilic pyrococcus and the antigenic shift are the result of natural selection and genetic drift.
However, the genetic bottleneck can be effectively explained with the following diagram.
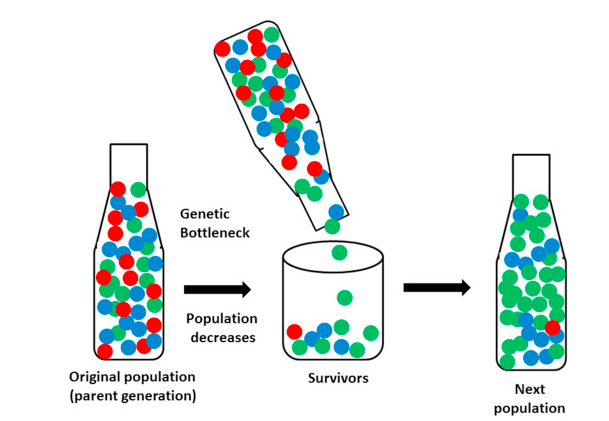
The first bottle entails the original population, which possesses different types of colors. However, in the case of a genetic bottleneck, the original size of the population will decline, and the given thing will completely change the genes of the new population. Thus, it is very right to say that genetic diversity is the result of the different environmental factors upon which an individual will not have any control.
2- Founder Effect
After the bottleneck, the founder is also regarded as another main effect that is related to genetic drift. Following the given context, it can be depicted that the founder effect tends to occur when a few members decide to start a new colony. The members who make this decision will belong to the original population. Thus, the given population will be very small. On the other hand, the given population may possess the following features, such as reduced genetic variation in comparison to the original population: Further, the nonrandom sample of the genes is also regarded as another significant feature of the small population.
Additionally, the given effect was outlined by Ernst Mayr in 1942. Here, it has used the existing theoretical work that was being developed by Sewall Wright. In addition to this, it can also be depicted that, due to the loss of genetic variation, the new population that has evolved will be distinctively different from the parent population in both a phenotypical and genotypic manner. However, in extreme cases, the founder effect will also lead to the subsequent evolution of the new species and speciation.
But the given thing can also be effectively explained with the help of the below-given diagram below.
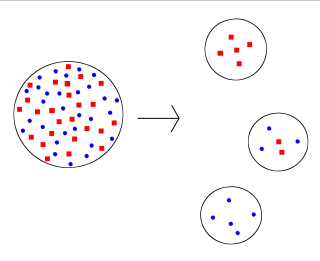
As you can see, there are four major circles. The very first circle is the whole population. It is also called by the name of the original population, which possesses an equal number of blue and red dots. But, in the founder effect, the new population will be regarded as very small. Thus, it is the reason why it tends to show increased sensitivity to genetic drift. Hence, it is another main effect that is associated with genetic drift effectively.
Also Read: Plant Physiology: Its role and explanation
Which Factors Cause Genetic Variation in the Population?
Genetic drift is a factor that creates differences between populations of the same species. This difference between the previous and current generations can be positive and negative. In most cases, these variances help in the survival and reproduction of species in the environment. In simple words, we can say that it helps with fertility and improves the survival of the population. The allelic effect is mainly known for its advantages, as it prepares one for unexpected things. So far, we have had the initial introduction of this drift, but have you wondered how fluctuations affect genetic variation? not yet. Below, we have discussed how genetic variation in a population is caused by multiple factors.
1- Random forces that lead to genetic drift
It is also being regarded as another big cause behind the occurrence of a situation like genetic drift in an effective manner. Therefore, it can be said that sometimes many random fluctuations tend to occur in the number of alleles in the population. The charges incurred by the relative allele are called genetic drift. However, genetic drift can be an increase or effectively decrease over some time. Mostly, the genetic drift occurs in a small population. This happens because, in a small population, there are greater chances of being lost. But, in comparison to this, in a large population, there are very few chances of being lost.
Moreover, the situation of genetic drift will remain until the allele that is involved in the population is completely lost or is fully involved with the present population. In both of the given conditions, there are very few chances of the occurrence of a condition like genetic diversity in the population in an effective manner. On the other hand, genetic drift is very common after the population experiences a situation like a population bottleneck.
2- The distribution also leads to genetic drift
This involves the physical distribution of people, which also has a significant impact on the population. In this context, it can be depicted that a species with a very broad distribution rarely has the same genetic makeup over the whole range. For example, some people live at a higher altitude and some live at a lower altitude. The alleles in the population in both situations will differ dramatically. Thus, in simple words, distribution is considered one of how genetic variation in the population can be preserved in the larger population. This will happen over a wide physical range.
Additionally, if an individual in any of the given ranges, such as high and low altitudes, reconnects and starts mating, then in this situation, the given thing will result in genetic intermixing. This will contribute to more genetic variation in an effective way. Overall, it is very right to say that genetic drift is also the result of how the whole population is distributed.
3- Migration also leads to genetic drift
It can be called the last cause that will lead to a condition like genetic drift effectively. Migration is defined as the movement of an individual (an organism) from one place to another. However, the given thing can also occur in a cyclical pattern. In this regard, if an individual who is migrating from one place to another forms a relationship with the destination individual, then the given type of condition will lead to a sudden influx of alleles. Here, when the migrated individual mates with the destination individual, in this situation, the migrated individual will carry the alleles of a specific individual who belongs to the destination place. Thus, due to the given situation, a significant change can be seen in the alleles of the population where the migrated individual stays.
Overall, it is very correct to say that these are all being regarded as some of the major causes that lead to genetic drift. Proper care should be assured about the same, to maintain proper balance about alleles in the population in an effective manner.
4- Matting pattern leads to genetic drift
It is being considered the very first reason behind the occurrence of a situation like genetic drift. Herein, it can be depicted that a nonrandom type of mating tends to occur when an organism chooses to mate with others based on a specific type of trait. Hence, in the given type of circumstances, an individual will make a variety of behavioral choices. The given types of choices will give shape to the genetic combinations, and thus they will appear in successive generations. If the given type of thing happens, then in this condition, the population pattern of matting will no longer be considered random.
There are two forms of nonrandom mating: inbreeding and outbreeding. Following the given context, it can be said that inbreeding is the type of breeding in which two people who have similar genes mate with each other. Consequently, outbreeding is a form of mating in which two individuals who belong to varied genotypes will mate with each other. From the given thing, it is very correct to say that inbreeding will lead to reducing genetic variation, or genetic drift. But, in comparison to this, a high number of generic variations are being seen in conditions like outbreeding.
Also Read: Current Biology Research Topics for Students
The Distinction between Genetic Drift and Mutation
Genetic drift and mutation are the two terms that often confuse students with their learning. To score good marks, they start searching, can someone do my online class on Google? With this search, they find reliable online class helpers to help them with their online classes. In this blog post, we will try to clarify the difference between these two theories. There is a significant difference that tends to exist between genetic drift and mutation. But the given things can be effectively explained in the below table:
| GENETIC DRIFT | MUTATION |
| It accounts for the random changes in the allergic frequency by chance. In simple words, it can also be said that there is a chance of eliminating some alleles and performing the fixation of some alleles. | It is the form of genetic material that leads to the phenotype and genotype of the organism. It is caused by the varied types of factors, which are called mutagens. |
| Environmental factors, migration, and nonrandom factors are being considered as the main causes behind the genetic drift. | Radioactive material change and X-rays are regarded as two main causes that will lead to the result, like mutation. |
| This will occur in small populations, and it also provides diversity without any kind of adaptation. | It includes different physical and chemical factors that lead to changes in the genes of the population. |
Who Are We
Can someone take my online test for me? Is there anyone who could help me with my introduction to anatomy and physiology coursework? Are these questions pondering in your mind? All Assignment Help is a website that is your answer to all of these questions. We have expertise in providing the best academic assistance to students worldwide. Whether you need assignment help, coursework help, or assistance with your online classes, we can assist you with all of your academic requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
| Question 1: What kinds of genetic drift are there? Answer 1: There are two types of genetic drift. They are the founder effect and the bottleneck effect. |
| Question 2: Who discovered the founder effect, and when was this effect discovered? Answer 2: The founder effect was coined by Ernst Mayr, a renowned taxonomist and leading evolutionary biologist. It was first founded in 1942. |
| Question 3: How is genetic drift different from gene flow? Answer 3: Gene flow is considered the flow or movement of genes, while generic drift studies the random change in the genes of a specific group of populations. |
| Question 4: Does the sewall wright depend on an allele’s beneficial or harmful effects? Answer 4: No, genetic drift does not depend on an allele’s beneficial or harmful effects, and the drift changes allele frequencies purely by chance. |
