Table of Contents
Hello folks! We are here again with a new blog post. If you’ve been struggling to understand English techniques, worry no more! This blog post is tailor-made for you. By the time you finish reading the post, you will have a much better understanding of these techniques.
But wait, there’s more! While understanding them is crucial, applying them practically is a whole different ball game. Don’t worry, We have a solution for that too. Once you’ve gained the knowledge from this blog, consider seeking expert help from AllAssignmenthelp. They can guide you on the proper usage of these techniques, helping you make optimum use of them in no time.
So, let’s read this blog, level up your English skills, and then take help from professionals to master the art of using these techniques effectively.
Meanwhile, let me tell you the contents of this blog post. We are going to have a brief description of:
- What are English Techniques
- Types of English Techniques
- How to use English Techniques
Let’s move to the meaning of English Techniques
What Are English Techniques?
Many of us are able to answer the question ‘What are English techniques.’ Generally, we don’t have many problems by giving a few names such as allegory, satire, parody, etc. But have you ever thought about how many of us know the actual purpose of using English techniques in a written text?
Well, some of us think that these English techniques add a kind of artistic value to the text. It is right also, but can you define what English techniques are? If not, then read below:
English Technique Definition:
English techniques, often referred to as literary or rhetorical techniques, are strategies that writers and speakers use to convey their ideas, evoke emotions, and engage their audience. These techniques enhance the effectiveness of communication and contribute to the overall impact of a piece of writing or speech.
Read More: What to Include in Resume?
Types of English Techniques
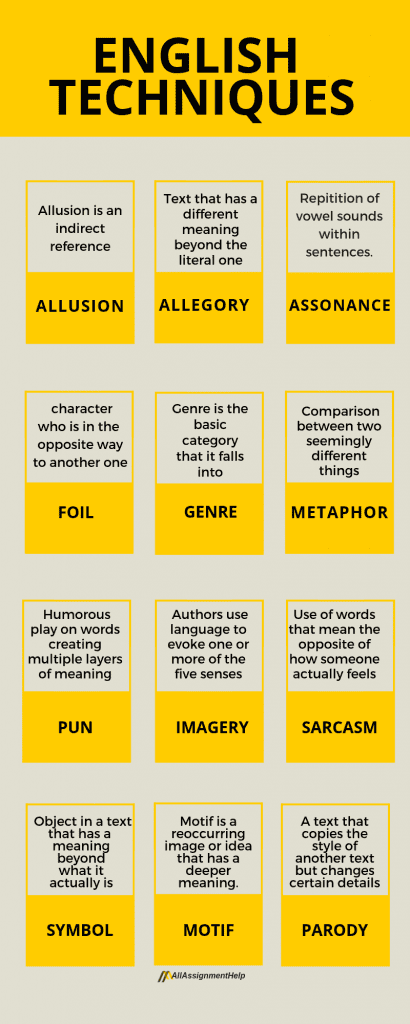
1. Allegory
An allegory is a type of text that has a different meaning beyond the literal one. Most often, allegories are used to express political situations or morals.
For instance: Young Goodman Brown written by Nathaniel Hawthorne is an example of allegory as it uses the Devil’s staff to defy God and eat the forbidden fruit.
Tip: Have a thought. Are you able to analyse a deeper meaning of the whole story? If yes, then it may be an allegory.
2. Allusion
It is an indirect reference. Most often, the authors allude to things like politics, culture, history and other works of literature.
For instance: When the volcano erupted, the forest was swallowed up in ash and dust like Jonah.” In the Bible, Jonah was swallowed by a whale.
Tip: Do you recognise a reference as being familiar? Congratulations, you caught an allusion!
3. Assonance
Assonance is the repetition of vowel sounds within a sentence. Along with consonance, it is a common technique used majorly in poetry.
For instance: Rhea thought she lost her father’s ring, Joseph.
Tip: You can identify assonance, where the vowel sounds rhyme but the endings do not.
4. Characterisation
Characterisation is the way in which a writer describes a character in the whole text. This can be done directly, in which the writer simply says that a certain character has a particular trait, or indirectly, in which the writer conveys what a character does, and you draw your conclusions.
For instance: Rebecca is a soft-spoken girl. She has issues in talking to boys, and never talks too much up in class. The writer has characterised her as being shy.
Tip: Are you learning some or other things about a character’s personality? If yes, then the character is being characterised.
5. Foil
A foil is a character who behaves the opposite way in comparison to the other characters in a text. Such a character usually foils the protagonist. However, it is necessary to understand that this does not imply that the foil is the antagonist. In fact, he or she can often be the protagonist’s close friend or family member. This character exists to draw attention to the traits of the character that they are foiling.
For e.g: Fredrick is wild and straightforward. His best friend, Edward, is simple and boring. You’ll notice Fredrick’s reckless behaviour even more because the difference between him and Edward is so huge.
Tip: Does this character highlight some other character’s traits because both of them act differently? If yes, then he or she is a foil.
6. Genre
The genre of a story is the basic category that it falls into. Common genres include science fiction, fantasy, romance, historical fiction, and non-‐fiction. Storytelling elements and devices like mood, style, tone, and theme all contribute to the genre.
For instance: Many of Edgar Allan Poe’s works are horror stories. This is because they carry suspense and has a dark set-up. Also, they deal with things like madness and death.
Tip: Every story around us has a genre. It’s up to you how to figure out which one it is. Focus at the subject matter, the things and other relevant literary devices to find some clues.
7. Motif
Definition: A motif is a reoccurring image or idea that has a deeper meaning. Among the other English techniques, this one is slightly stronger than a symbol as it occurs more than once, but not quite as big as a theme, although it might contribute to the theme.
For instance: Jack goes on a journey alongside a forest, and he continues to see owls as he travels. Every time he sees one, he reminds his mother who told him that owls are a sign of wisdom and good fortune.
Tip: If you keep finding the same object throughout the text and it seems to be important, it’s probably a motif.
Struggling with your online English classes? Receive instant assistance from professional writing experts and excel with flying colours. Simply reach out to us and say, “Take my online English class for me,” allowing the experts to manage all your stress.
8. Onomatopoeia
Onomatopoeia is referred to as words that sound like the noises they express.
For example Words like splash, babble, boom, buzz, crash, sizzle, warble, gurgle, hiss, mumble and zap.
Tip: If the noise’s name sounds like the noise itself, it’s onomatopoeia.
9. Stream of consciousness
Authors use a stream-of-consciousness style of writing to mimic the way we think inside our own heads. This technique often ignores normal punctuation and grammatical structure.
For instance: Okay, while I’m at the store I need to pick up milk, birthday candles, and…ugh, what else? Oh yeah, flowers! I hope Lynette likes roses. Did I make our dinner reservation yet? I should call to confirm. Ah, here are the candles!
Tip: Are the character’s thoughts jumping from place to place in a rapid way that doesn’t totally make complete sense? If so, the author is using a stream of consciousness.
10. Parody
A parody is a text that copies the style of another text but changes certain details in a humorous way in order to draw attention to how absurd they are. The difference between parody and satire is that satire is more critical while parody is usually done just for laughs.
For instance: Pride and Prejudice and Zombies is a book that incorporates zombies into Jane Austen’s world.
Tip: Does the text make you laugh because it’s an exaggerated imitation of something else? It’s probably a parody.
11. Satire
Satire is the comedic ridicule of someone’s flaws or shortcomings in order to draw attention to a specific issue. The difference between satire and parody is that typically, parodies are strictly meant to be funny while satire often attempts to supplement the humour with a call to action to create social change.
Example: Saturday Night Live is full of skits that satirise political figures. The cast of the show dresses up as people such as Barack Obama and Hillary Clinton and then mocks their speech patterns and mannerisms in a way that is lightly critical.
Tip: If it makes you laugh but also makes you question what exactly is being made fun of and why it’s satire.
12. Pathetic fallacy
Pathetic fallacy is the attribution of human traits to non-‐humans, especially the weather or other elements within nature. It is a type of personification.
For instance: The dark, heavy clouds looked pregnant with rain.
Tip: Is a natural phenomenon being described in a human way? The author is probably using a pathetic fallacy. Also, keep in mind that “pathetic” here does not mean sad and pitiful.
13. Simile
A simile is a comparison between two seemingly unlike things that use words such as “like,” “as,” or “then.”
For instance: She was as welcome as a fart in an elevator.
Tip: If you see two different things being compared and the words “like” or “as” between them, it’s probably a simile.
14. Metaphor
A metaphor is a comparison between two seemingly different things. You are encouraged to notice the resemblance between these objects because one word or phrase is literally replaced by another word or phrase.
For instance: The child was a monkey, climbing all over the table and chairs and screaming at the top of his lungs.
Tip: If what’s being described is not literally happening but instead makes a judgement on the similarity between the two things, that’s a metaphor.
Difference between simile and metaphor
mostly, people confuse between simile and metaphor, if you also find them alike then let me tell you that they are very different from each other, here is the difference:
A simile is a comparison using the word “like”, for example: as light as a feather. This sentence is comparing the light of something with a feather. Whereas in a metaphor, you say that something is something else. For example, You lit up my life. This sentence is simply saying that someone is bringing them joy.
15. Verse
Verse is a form of writing in which the structure of the text is just as important as the text itself. Those who write verse will pay attention to things like rhyme scheme and meter, while those who write in prose will not.
For instance: I think that it could be worse, but these lines are a nice little clue, of what verse should look like to you!
Tip: It’s probably versed If it’s written in anything besides paragraphs
16. Truncated sentence
Truncated sentences are a kind of shortcut that writers use when the rest of a sentence’s meaning can be implied.
For example: If you say, “I like dogs more than Jane,” you’re most likely meaning that you adore dogs more than Jane likes cats. Not that you don’t like Jane.
Read More: Things to Ponder About Human Resource Management
17. Zeugma
Zeugma is when the author uses a word that has numerous meanings for different phrases in the same sentence.
For instance: Jennet lost her purse and her mind. “Lost her purse” literally means that she misplaced it, however, “lost her mind” means she went crazy and is a figure of speech.
Tip: Did you pause for a while to be sure that you read it right because the phrases didn’t quite flow? The writer might have used zeugma.
18. Tone
The tone is a way that the writer or a character shows an opinion towards something. Tone can be both negative or positive, but it can also be other things such as satirical, light-‐hearted, nostalgic or reverent.
For instance: The tone in a news article should be natural and neutral both because a journalist doesn’t intend to sway the readers’ opinions.
Tip: The language that is utilised will give you a clue about the way a writer or speaker feels.
English is complex; students studying literature must grasp its basics for flawless writing. Struggling with tones? Seek our online English assignment help. With our expert’s help, you can enhance your grasp of English, resolve doubts and improve your command of the language.
19. Symbol
A symbol is an object in a text that has a deeper meaning beyond what it actually is. The English techniques of using symbols can be seen in some classic symbols like certain flowers, colours, foods, and the weather, but writers often make symbols that are particular to individual stories.
For instance: Water is often linked to things like purity, cleansing, and rebirth.
Tip: Most of the stories have different symbolic items throughout. Though, don’t be too eager to try too hard to find out them. At times a red curtain is red just because the writer felt like it. Most often, symbolism is fairly obvious in most of the texts.
20. Sarcasm
Sarcasm is the use of words that mean the opposite of how someone actually feels, usually either to show disdain or to achieve a comedic effect.
For instance: I just love getting stuck in the crowd. It is the best feeling ever!
Tip: It can be tough to catch sarcasm in written form, so don’t worry too much, but if it appears that a character is mocking another person, it is probably sarcasm.
21. Metonymy
Metonymy is the act of referring to an object or something by a closely related object rather than by its own name.
For instance: Saying that “We will swear loyalty to the crown” doesn’t mean that people are going to be ruled by a crown and consider an object as their leader. It means the people are addressing a royal person.
Tip: Do not confuse yourself if the literal meaning sounds slightly off, it’s metonymy. Synecdoches are exceptions, so work on identifying the difference between both.
22. Juxtaposition
Juxtaposition is when two different objects or concepts are placed near each other. This is usually done to highlight the differences between them, much like how a foil works. Juxtaposition can appear as an element of the story or part of the writing itself.
For instance: A wealthy person is having a lavish party that displays tons and tons of wastefulness, and across the street, there is a poor family who is struggling to survive.
Tip: If you can see the differences between two things more clearly after they’ve been thrown together, it’s because they were juxtaposed.
23. Foreshadowing
Foreshadowing is when the author drops hints about something that will be more meaningful later in the story.
For instance: Fred mentions offhand that he’s allergic to peanuts in chapter two. In chapter nineteen, he is accidentally served something with peanuts in it and almost dies.
Tips: You might not necessarily notice that something is foreshadowing when you first read through a text, but once you know the ending, it should be pretty clear.
24. Imagery
Imagery is when authors use language to evoke one or more of the five senses in a strong, descriptive way.
For instance: He was so distracted by the warm, sweet smell of baking cookies that he tripped and fell down the rough stone staircase.
Tip: Can you almost see, smell, touch, taste, or hear what’s happening? If so, the author used very vivid imagery.
25. Pun
A pun is a humorous play on words that creates multiple layers of meaning in a sentence.
For instance: Did you hear about the psychic dwarf who escaped from prison? They say that there’s a small medium at large.
Tip: If it makes you laugh and groan at the same time, it’s a pun.
f what verse should look like to you!
Tip: It’s probably versed If it’s written in anything besides paragraphs.
These linguistic strategies help students in achieving high marks in writing exams. You can easily achieve a decent grade in exams if you have a solid command of linguistic skills.
How to Use English Techniques?
The time has come for you to use these strategies in your writing. We believe you comprehend a basic understanding of the tactics of the English language. Once you’ve read about every English technique, you’re ready to practice using them.
Now, that you have read about all the English techniques, it’s time to know how to use them.
Be Natural
Whenever you write, you’re using English techniques– even if you are not aware of this fact! This is because there are some English techniques which are naturally a part of everyday speech. This is why they come into our writing as well. So, what you need to do is to don’t fill them forcibly in your text. They will come into it naturally.
Readout carefully
You must be having some favourite writers. Go through their work in a bit serious manner. Well, I am not saying that you are not a good reader. Just asking you to focus on identifying the English techniques while reading. Every writer uses the above-listed English techniques.
You just have to pay close attention to them. You will have to keep track of the English techniques while you read them. As you get good at identifying literary devices, try to see how they are used. Check out how the writer uses many English techniques to contribute to the overall effect of the story or poem in the written text.
Give time to learn English techniques
The English techniques have their own tricks and advantages. Trust me; no one is perfect in all the techniques. The only way to learn perfectly is to keep practising. Be patient, and continue to practice. You will surely improvise steadily. Try to learn a new English technique in a definite interval, say in a week. Along with this incorporate it into your own daily writing.
These are some fundamental guidelines that you should adhere to when writing. But keep in mind that we are here for you at every step.
If you enrol in an online English course, we can also be a helping hand to you. Just come to us and say take my online class for me our team of experts will do their best to resolve all your queries and subject-related issues
Conclusion
English techniques can also be referred to as literary linguistics or literary elements. They are the best technique to make any written piece equally engaging and persuasive. Continue learning about these tactics and putting them to use in your everyday writing if you want readers to identify the content you are writing.
Alliteration, simile, metaphor, pun, juxtaposition, and other English literary techniques enhance the text’s meaning. You already have a quick description of how to use them from this blog post. There are only three things to keep in mind when writing: write naturally, read everything you read carefully, and continue to hone your English skills.
Visit Allassignmenthelp When You Are In Need
If there is still some confusion in understanding the English techniques, you can come to AllAssignmentHelp.com and clear them. We have a team of expert academic assignment writers, who can help you with every academic check. All you need to do is to connect with us. You can do this over a call or by simply leaving a message.
So, if you are facing any issues related to the writing process, bring them to us. We offer top-notch assignment help to enhance your writing skills. Our writers provide custom guidance and valuable tips for developing better writing skills. Trust our reliable team for excellent assignment help services. Stay connected and thank you for your support.
FAQs
| Ques.1. What makes learning English language techniques important? Answer: Learning English language techniques enhances communication, writing, and critical thinking skills. It aids effective expression, enables nuanced interpretation, and fosters cultural understanding, vital in academia, careers, and daily life. |
| Ques.2. Where can I find language strategies? Answer. A linguistic strategy can be found in almost any place in a tale, novel, poem, or essay. Assonance, idioms, personification, imagery, proverbs, onomatopoeia, imperative, and other linguistic devices are crucial in English. |